Central Sleep Apnea: Types, Causes, Symptoms, Risk, Diagnosis and Treatment
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Central sleep apnea (CSA) is a sleep disorder that affects a small percentage of the general population. In India, it's a rising health problem due to obesity and lifestyle changes.
Central sleep apnea (CSA) is a sleep disorder that occurs when the brain doesn't send the right signals to the muscles that control breathing. This results in breathing that stops and starts repeatedly during sleep. In this blog, we’ll explore what central sleep apnea is, its causes, types, symptoms, diagnosis, the available treatments and some tips to help you better understand this condition and how it can be managed.
What is Central Sleep Apnea?
Central sleep apnea is a sleep disorder where your breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep due to a failure in the brain's signals to the muscles that control breathing. Unlike obstructive sleep apnea, which occurs when the muscles in the throat relax and block airflow, central sleep apnea is caused by a problem in the brain's respiratory control center.
During episodes of CSA, your body may temporarily stop breathing for 10 seconds or more, causing drops in blood oxygen levels, which can disrupt sleep and lead to other health complications.
Types of Central Sleep Apnea
Central sleep apnea happens when your brain doesn't send the right signals to your muscles that control breathing while you sleep. There are different types of central sleep apnea, each with its own cause:
Cheyne-Stokes Breathing
This type involves a pattern of breathing where you breathe very deeply, then your breathing becomes shallow or stops for a while, and then it starts again. This cycle repeats throughout sleep. It is often seen in people with heart problems or other serious illnesses.
Idiopathic Central Sleep Apnea
This type has no known cause. It just happens for reasons that doctors can’t fully explain. It’s not linked to heart failure or other obvious conditions.
Central Sleep Apnea Due to Medical Conditions
Some conditions, like heart failure or certain neurological disorders, can cause central sleep apnea. In these cases, the apnea happens as a result of the medical condition affecting how the brain controls breathing.
Central Sleep Apnea Due to a Medication or Substance
In some cases, when certain medications or substances are used, they can interfere with the brain's ability to properly initiate and regulate breathing. It is seen that Opioids such as methadone trigger central sleep apnea in many individuals.
Causes of Central Sleep Apnea
Central sleep apnea is usually related to underlying health conditions or disruptions in the body’s control of breathing.
Some common causes include:
- Heart Failure: One of the most common causes of CSA is congestive heart failure (CHF). When the heart is unable to pump blood efficiently, it can affect the brain’s ability to regulate breathing during sleep.
- Brain Stem Injury or Damage: The brain stem controls basic functions like breathing. Damage to this area from injury, stroke, or certain diseases can impair the brain's ability to send proper signals to the breathing muscles.
- High Altitude: Sleeping at high altitudes can trigger CSA due to lower oxygen levels, which can interfere with your body’s natural breathing rhythm.
- Complex Sleep Apnea Syndrome: This is a combination of obstructive sleep apnea and central sleep apnea. It can develop after someone is treated for OSA with a CPAP machine, but CSA persists.
- Other Medical Conditions: Certain neurological conditions like Parkinson's disease or other respiratory diseases can also contribute to CSA.
Symptoms of Central Sleep Apnea
The symptoms of central sleep apnea may not always be immediately obvious, and many people with CSA are unaware they have it.
However, common symptoms include:
- Frequent waking up during the night: You may wake up gasping for air or feeling short of breath.
- Insomnia or poor-quality sleep: This happens because your body is repeatedly waking up due to interrupted breathing.
- Excessive daytime sleepiness: This is a common result of disturbed sleep patterns.
- Morning headaches: Lower oxygen levels during sleep can lead to headaches when you wake up.
- Difficulty concentrating: Poor sleep can impair cognitive function and memory.
- Snoring: Although more common in obstructive sleep apnea, some individuals with CSA may also snore, but it is often less pronounced.
If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it's important to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Risk Factors for Central Sleep Apnea
It is seen that there are certain factors that can increase your chances of developing central sleep apnea such as:
- Medical Conditions: There are a number of medical conditions such as heart failure, stroke, kidney failure, atrial fibrillation, excessive growth hormone production, spinal cord injuries and certain metabolic disorders that can increase your risk of central sleep apnea.
- Age: The risk of central sleep apnea increases as you age, it is seen that CSA occurs more commonly in individuals over the age of 65. As you age, there is higher risk of heart failure, diseases of the brain, irregular heartbeats, diseases of blood vessels and sleep disorders.
- Medications: A number of medications such as opioids, antidepressants, benzodiazepines, anticonvulsants and certain relaxants and antiplatelet medications can increase the risk of central sleep apnea.
- Sex: It is seen that sleep apnea is more common in men as compared to women. The reason behind this could be the effects of testosterone on the amount of carbon dioxide that can accumulate in the blood before the body reflexively takes a breath.
Diagnosing Central Sleep Apnea
If your doctor suspects you have central sleep apnea, they will likely recommend a sleep study.
There are two main types of sleep studies:
- Polysomnography (In-lab Sleep Study): This is the most comprehensive test where sensors are attached to your body while you sleep, monitoring brain activity, heart rate, breathing patterns, and oxygen levels.
- Home Sleep Apnea Test (HSAT): This at-home test is less extensive but can still measure your breathing patterns, oxygen levels, and other key factors related to sleep apnea. It’s often used if CSA is suspected to be related to other conditions like heart failure.
Treatment Options for Central Sleep Apnea
Treatment for central sleep apnea focuses on managing the underlying causes of the condition and improving sleep quality.
Here are some common treatments:
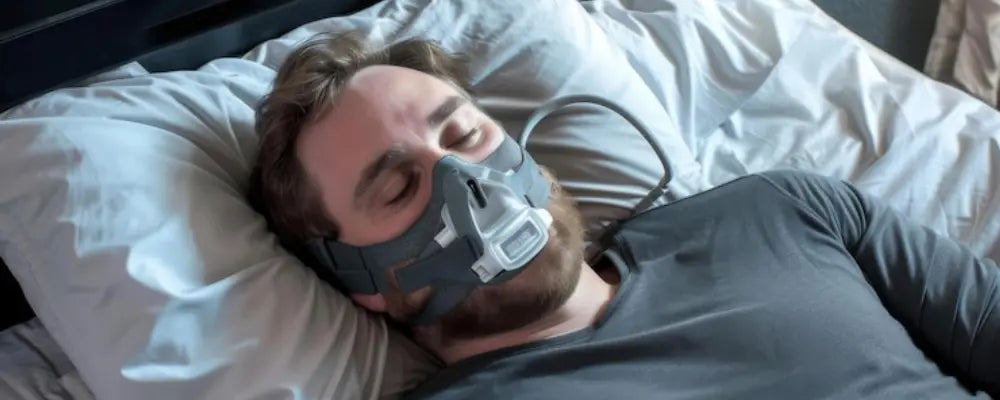
Positive Airway Pressure (PAP) Devices
- Adaptive Servo-Ventilation (ASV): ASV is a special device that adjusts pressure levels based on your breathing patterns. It’s commonly used to treat central sleep apnea, especially in patients with heart failure.
- Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP): This device provides different air pressure levels for inhaling and exhaling, helping regulate your breathing during sleep.
Medications
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help stimulate breathing. Drugs like acetazolamide can help improve respiratory function by adjusting your body's response to oxygen and carbon dioxide levels.
Treating Underlying Conditions
If CSA is caused by a heart condition, managing heart failure with medications, lifestyle changes, and possibly surgery may improve breathing patterns. Similarly, addressing neurological or other health issues contributing to CSA is important.
Lifestyle Changes
While lifestyle changes alone may not cure CSA, they can help improve overall sleep and health. This can include:
- Weight management (if needed)
- Regular exercise to improve heart health
- Reducing alcohol consumption and avoiding sedatives, as they can relax the muscles involved in breathing control
- Sleeping on your side, as sleeping on your back may worsen breathing issues
Oxygen Therapy
There are people who suffer from sleep apnea because there is very low oxygen level during sleep, in such cases supplemental oxygen may be recommended to make sure there is enough oxygenation throughout the night.
Also Read:- How Weight Affects Sleep Apnea
How to Live with Central Sleep Apnea
After being diagnosed with central sleep apnea people get a little relief as now there is a reason behind their symptoms, but it can also be a challenge to live with it when you have conspicuous treatment going on.
Here are a few tips that can help you live with central sleep apnea:
- Be Informed about your condition: It is very important that you learn about your symptoms and the best possible treatment options available for you. If you have any questions, always ask your doctor first. If you are diagnosed with sleep apnea or any other sleep disorder, you may also find some websites and support groups very helpful.
- Be in touch with your doctor: After being diagnosed with CSA or any other sleep disorder, it is important that you follow-up with your doctor on regular intervals. Keep your doctor informed about your symptoms, if your current treatment is effective or if you are having any complications or side effects of treatment.
- Avoid anything that triggers sleep apnea: There are some lifestyle factors or sedatives such as alcohol and opioids that can trigger episodes of abnormal breathing. Always consult your doctor before taking anything or expose yourself to factors that can lead to sleep apnea or sleep disorders.
When to Seek Medical Help
If you suspect you have central sleep apnea, it’s important to see a doctor. CSA can lead to serious complications like high blood pressure, heart failure, stroke, and even sudden death if left untreated. A healthcare professional can help determine the cause of your sleep apnea and recommend appropriate treatments.
Conclusion
Central sleep apnea is a serious but treatable condition that affects your ability to breathe while sleeping. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, you can take the necessary steps to improve your sleep and overall health. If you experience symptoms such as frequent awakenings, daytime fatigue, or difficulty concentrating, it is important to consult with your doctor so that your condition can be diagnosed and treated effectively.